How Crypto Spoofing Really Works (With Case Study).

Cryptocurrency spoofing is a deceptive tactic where traders place large buy or sell orders they don't intend to execute, aiming to manipulate market prices for personal gain. Recognizing these schemes is crucial for investors to protect their assets.
Understanding Crypto Spoofing
In crypto markets, spoofers create an illusion of supply or demand by placing significant orders without the intention of fulfilling them. This manipulates prices, allowing spoofers to profit at the expense of other traders.
Identifying Crypto Spoofing: Key Indicators
- Large, Unfilled Orders: Watch for substantial buy or sell orders that remain unexecuted and are quickly canceled once the market moves in the desired direction.
- Order Book Imbalances: A sudden disparity between buy and sell orders can signal spoofing.
- Rapid Order Placement and Cancellation: Frequent addition and removal of large orders within a short timeframe may indicate manipulative intent.
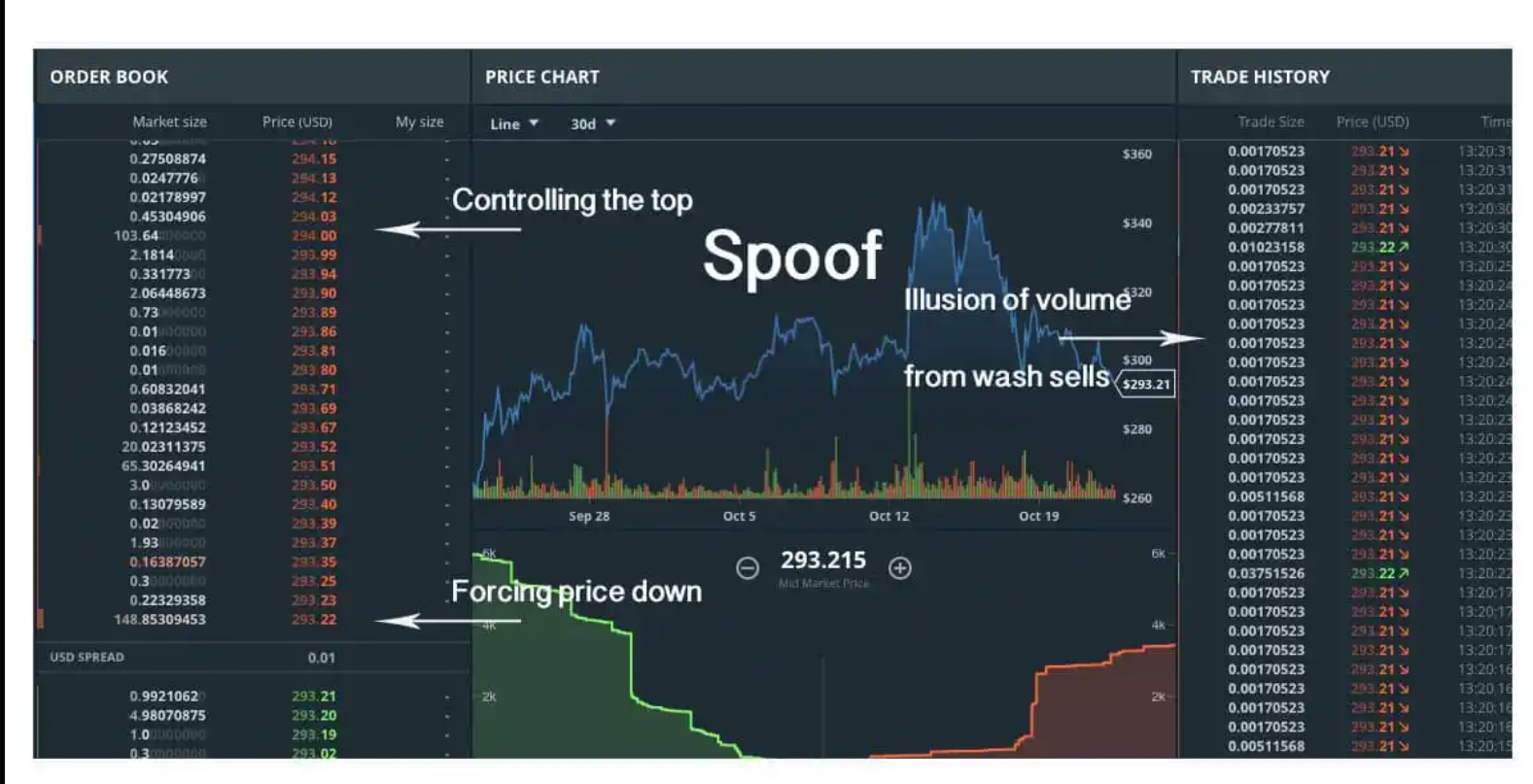
This image illustrates crypto spoofing, a market manipulation tactic where traders place large buy or sell orders without the intention of executing them. This deceives other traders into reacting to fake supply or demand, influencing the market price.
Key Elements in the Image:
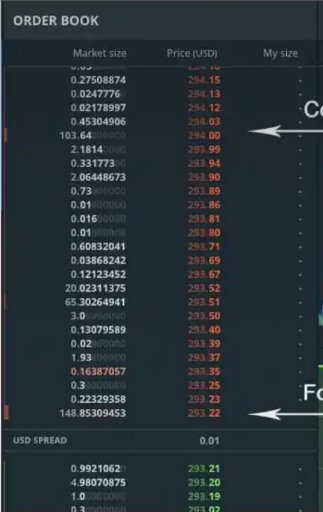
- Order Book (Left Side)
a. Shows a large number of orders stacked at different price levels.
b. Spoofing tactic: A trader places massive sell orders at the top without executing them to create fake selling pressure, making it appear as if prices will drop.
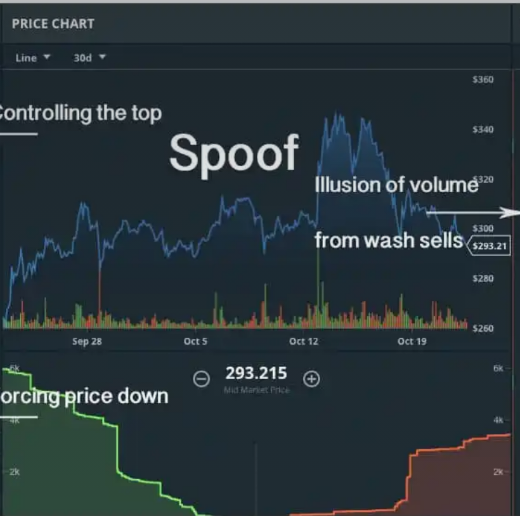
2.Price Chart (Middle)
a."Controlling the top" – The spoofer manipulates the price by setting a false resistance level.
b."Illusion of volume from wash sells" – Some transactions are made between related accounts to fake volume and increase credibility.
c.Sharp price movements indicate artificial volatility.
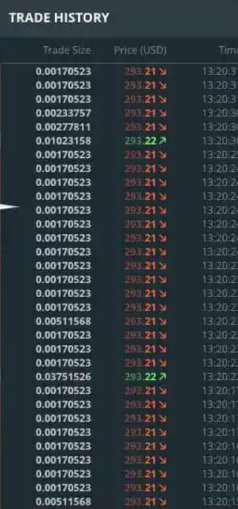
3.Trade History (Right Side)
a.Displays actual executed trades.
b.Small trade sizes show possible wash trading, where the same entity buys and sells to itself.
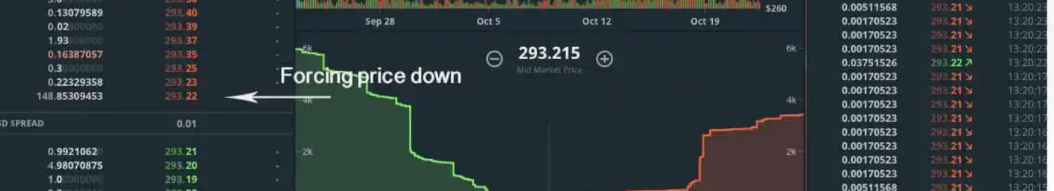
4.Depth Chart (Bottom)
a.The green section represents buy orders (support).
b.The red section represents sell orders (resistance).
c."Forcing price down" – A large wall of fake sell orders pressures traders to panic-sell, driving prices lower.

Real-Life Example: The 2018 Bitcoin Spoofing Incident
In 2018, a trader was charged with manipulating Bitcoin prices through spoofing. The trader placed large orders to create a false impression of demand, influencing prices and profiting from the resulting market movements.
Bitcoin Price Movement During the 2018 Spoofing Incident
Preventive Measures for Traders
- Utilize Advanced Trading Tools: Employ platforms that offer real-time order book analysis and alerts for suspicious activities.
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of regulatory developments and market news to recognize potential manipulation tactics.
- Exercise Caution: Be wary of sudden market shifts without clear reasons, as they could result from spoofing.
Conclusion
Understanding and identifying spoofing is vital for maintaining the integrity of cryptocurrency trading. By recognizing the signs and staying vigilant, traders can better protect their investments and contribute to a fairer market environment.
