[Masterclass] Crypto Market Manipulation: Unmasking Pump-and-Dump, Wash Trading, and Whale Tactics
![[Masterclass] Crypto Market Manipulation: Unmasking Pump-and-Dump, Wash Trading, and Whale Tactics](/content/images/size/w1200/2025/03/Pump-and-Dump--Wash-Trading--and-Whale-Tactics.png)
Crypto Market Manipulation: Pump-and-Dump, Wash Trading, and Whale Tactics Explained
Cryptocurrency markets are infamous for their volatility. While natural market dynamics play a role, deliberate manipulation often exacerbates price swings. Three of the most prevalent manipulation tactics include pump-and-dump schemes, wash trading, and whale manipulation. This article breaks down these strategies, offering real-world examples, the psychological factors that fuel them, and the regulatory efforts to curb them.
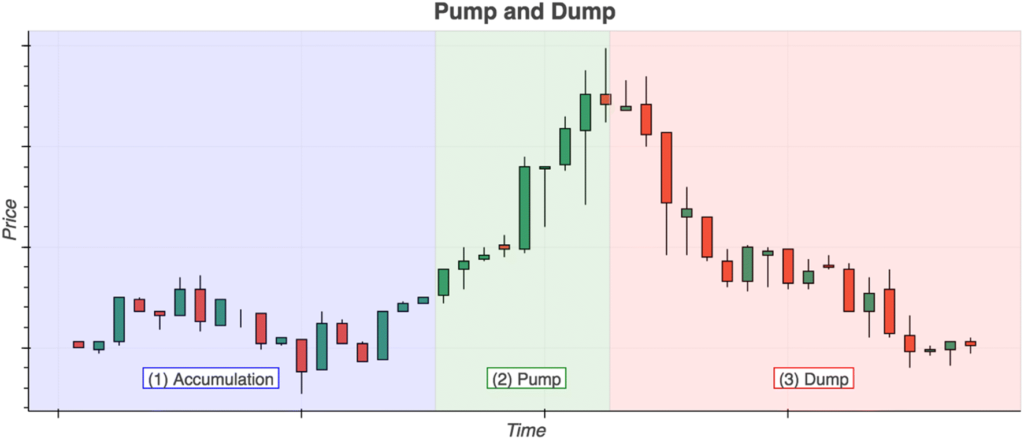
1. Pump-and-Dump Schemes
A pump-and-dump scheme involves artificially inflating the price of a cryptocurrency (the "pump") before selling off at the peak (the "dump"), leaving unsuspecting investors with losses. These schemes are commonly orchestrated in online groups on platforms like Telegram and Discord, where organizers coordinate mass buying of low-cap coins while aggressively promoting them on social media. Once the price surges and attracts uninformed investors, insiders offload their holdings, triggering a sharp price collapse.
Historical Example: ICO Boom (2017–2018)
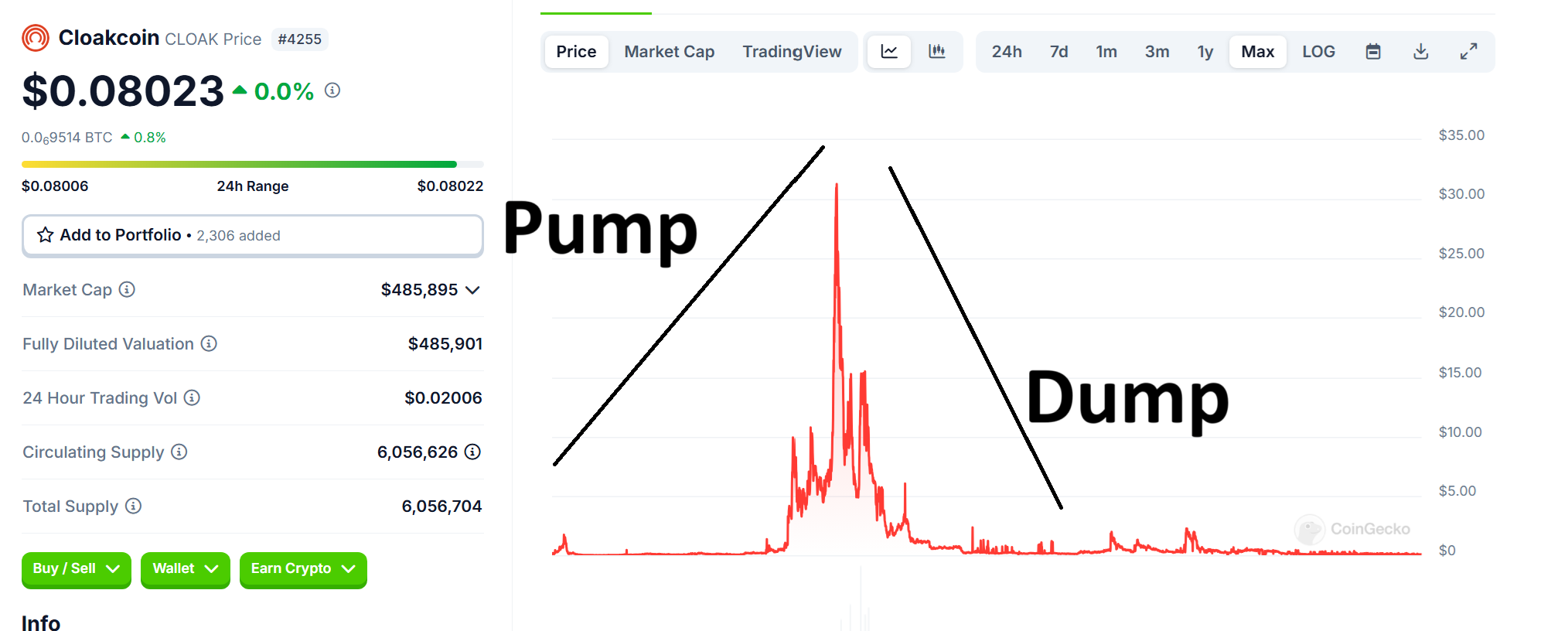
During the Initial Coin Offering (ICO)boom, pump-and-dump schemes flourished. A 2018 Wall Street Journal investigation revealed that groups like “Big Pump Signal” coordinated at least 175 such schemes across 121 cryptocurrencies. One notable case involved CloakCoin, where a pump group triggered a 50% price surge within minutes before a rapid crash, generating millions in artificial trading volume.
Recent Example: Meme Coin Mania & Legal Crackdowns
The rise of meme coins in 2021 demonstrated large-scale pump-and-dump dynamics. More recently, in October 2024, U.S. authorities charged 18 individuals in an international crypto fraud operation. These individuals manipulated token prices through false hype and coordinated trades, resulting in a multi-billion-dollar scam. This DOJ action signals growing regulatory attention toward such fraudulent practices.
Psychological Drivers
Pump-and-dumps exploit greed and herd mentality. Investors fear missing out (FOMO) on quick gains, leading them to buy into the hype. As the price rises, more people jump in, reinforcing the momentum. Once the orchestrators dump their holdings, fear takes over, leading to panic selling.
Regulatory Response
Regulatory agencies like the SEC and CFTC classify pump-and-dump schemes as market manipulation. In 2018, the CFTC explicitly warned that these scams are "old frauds in a new form." Enforcement actions have since ramped up, with multiple legal cases filed against crypto projects and influencers involved in coordinated pumps.
2. Wash Trading
Wash trading involves artificially inflating market activity by repeatedly buying and selling the same asset. This deception misleads traders into believing there is high liquidity or demand, enticing them to invest. Some exchanges use this tactic to boost rankings on platforms like CoinMarketCap, while projects employ it to create the illusion of popularity.
Historical Example: Fake Volume on Crypto Exchanges
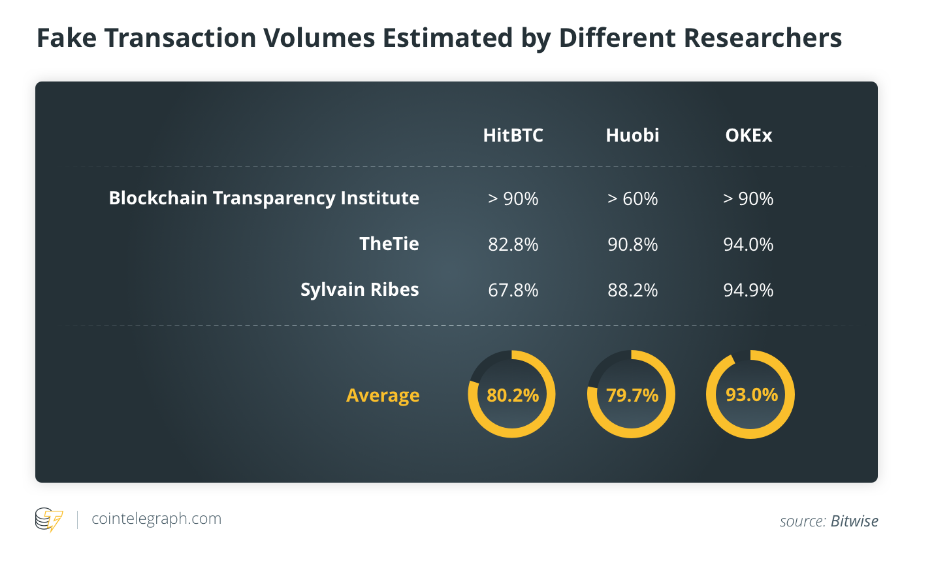
In 2019, a report by Bitwise revealed that 95% of reported Bitcoin trading volume was fake, primarily due to wash trading on unregulated exchanges. In 2020, South Korean exchange Coinbit was seized after an investigation found that 99% of its volume was fabricated through wash trades.
Recent Example: NFT Market Manipulation
Wash trading persists in the NFT sector. A 2022 study found that over 50% of NFT trading volume on Ethereum was fraudulent, with traders artificially inflating asset prices to attract real buyers. In some instances, 80% of daily trading volume was wash trades.
Psychological Drivers
Wash trading exploits the belief that high trading volume signifies a valuable asset. Investors assume liquidity and demand, triggering FOMO and leading to real purchases. In reality, the market interest is often fabricated.
Regulatory Response
Wash trading is illegal in traditional finance and is increasingly being prosecuted in crypto. The CFTC fined Coinbase $6.5 million in 2021 for misleading volume reports, while South Korean regulators have aggressively cracked down on fake volume practices.
3. Whale Manipulation
A "whale" is a large investor with the power to influence cryptocurrency prices through massive trades. Whale manipulation occurs when these investors strategically place large buy or sell orders to sway market sentiment, triggering herd reactions.
You can watch the entire sell and buy orders executing over time in the time-lapse video below.
Historical Example: Bitcoin’s "BearWhale" (2014)
In 2014, an anonymous whale placed a massive 30,000 BTC sell order at $300 on Bitstamp, causing panic among traders. Although the market eventually absorbed the sell-off, it highlighted how a single large trade could disrupt prices and investor confidence.
Recent Example: Whale-Induced Market Swings
Today, whales continue to manipulate markets by executing large trades that trigger automated stop-losses or buying during quiet periods to spark rallies. Some whales engage in "dump raids," selling large amounts to induce panic before rebuying at lower prices. Additionally, the 2024 DOJ investigation revealed whale-like activities, where market makers artificially pumped and dumped token prices.
Psychological Drivers
Whales manipulate markets by leveraging fear and greed. Large sell orders create panic, while aggressive buying generates FOMO. Traders monitor whale movements, often reacting impulsively to their actions, making them easy targets for manipulation.
Regulatory Response
While whale trading itself isn’t illegal, certain tactics like spoofing (placing orders with no intention of executing) are prohibited under U.S. law. The CFTC and SEC have prosecuted individuals for spoofing in Bitcoin futures markets, and international regulators are increasing scrutiny on large holders engaging in manipulative tactics.
The Psychology of Fear, Greed, and Herd Behavior in Crypto
At the core of these manipulation tactics are psychological biases that drive investor behavior:
- Greed & FOMO: Investors chase quick profits, making them vulnerable to fabricated price pumps.
- Fear & Panic: Sudden price drops or large sell orders can trigger herd-driven sell-offs.
- Herd Mentality: Many traders follow market trends blindly, assuming that if others are buying or selling, they should too.
Understanding these psychological triggers can help investors recognize manipulation and avoid being exploited.
Regulatory Oversight & Conclusion
As cryptocurrency matures, regulators are taking stronger actions to combat market manipulation. The SEC, CFTC, and DOJ have ramped up enforcement against pump-and-dump scams, wash trading, and whale manipulation. The October 2024 DOJ crackdown is a landmark case, showing that global authorities are serious about policing crypto markets.
For investors, the best defense is education and skepticism. If a cryptocurrency experiences an unexplained surge, if an exchange reports suspiciously high volume, or if a single wallet is moving markets, these could be red flags. In a market filled with manipulation, staying informed and critically assessing price movements can prevent costly mistakes.
By understanding pump-and-dumps, wash trading, and whale tactics, traders can navigate crypto markets with greater awareness and avoid falling victim to fraudulent schemes.
References
- Commodity Futures Trading Commission – Customer Advisory: Beware Virtual Currency Pump-and-Dump Schemescftc.gov (Feb 2018).
- Wall Street Journal via Cointelegraph – Organized Crypto “Trading Groups” Manipulated Markets to Make $825 Million in 2018cointelegraph.comcointelegraph.com.
- PYMNTS.com – Cryptocurrency Pump And Dump Schemes Growingpymnts.compymnts.com (Aug 2018).
- U.S. Department of Justice – Press Release: Eighteen Individuals and Entities Charged in International Operation Targeting Crypto Market Manipulationjustice.govjustice.gov (Oct 9, 2024).
- Marie Huillet, Cointelegraph – One Whale Was Behind Bitcoin’s 2017 Bull Run, Claim Researcherscointelegraph.comcointelegraph.com (Nov 2019).
- Bitcoinwiki – BearWhale entry (Bitcoin history anecdote)bitcoinwiki.org (Oct 2014).
- Merkle Science – Coinbit Seizure: Examining Why New Crypto Exchanges Conduct Wash Tradingmerklescience.commerklescience.com (July 2021).
- Marie Huillet, Cointelegraph – Bitwise Tells US SEC That 95% of Volume on Unregulated Crypto Exchanges Is Suspectcointelegraph.com (Mar 2019).
- Rosie Perper, CoinDesk – Over $30B of NFT Trading Volume on Ethereum Is Wash Trading, Research Suggestscoindesk.comcoindesk.com (Dec 2022).
- Reuters – CFTC orders Coinbase to pay $6.5 million for false reporting and wash tradingreuters.com (Mar 19, 2021).
